Code
def f(x):
return x**2 + 6*x + 9The majority of the text and code has been generated by AI.
Editor: Witek ten Hove
See book section
Relationship Between Mathematical Functions and Functions in Python
Mathematical functions and functions in Python share some fundamental concepts, but they are implemented and used in different ways. Understanding their relationship can help us leverage the power of Python libraries like SymPy for symbolic mathematics and visualization libraries for plotting.
1. Mathematical Functions:
In mathematics, functions are a fundamental concept that relates an input (or a set of inputs) to an output. A mathematical function typically takes one or more variables as inputs and produces a single output. Functions are often denoted by symbols like \(f(x)\) or \(g(x, y)\).
Example: Mathematical Function
\[f(x) = x^2 + 6x + 9\]
2. Functions in Python:
In Python, functions are blocks of code that perform a specific task. They can take input arguments and return a result. Python functions can be defined using the def keyword and can be called multiple times within a program.
Example: Python Function
3. Using SymPy for Symbolic Mathematics:
SymPy is a Python library for symbolic mathematics. It allows us to work with mathematical expressions in symbolic form, just like we do in mathematics. SymPy functions can be used to manipulate and simplify algebraic expressions.
Example 1: Plotting a Mathematical Function
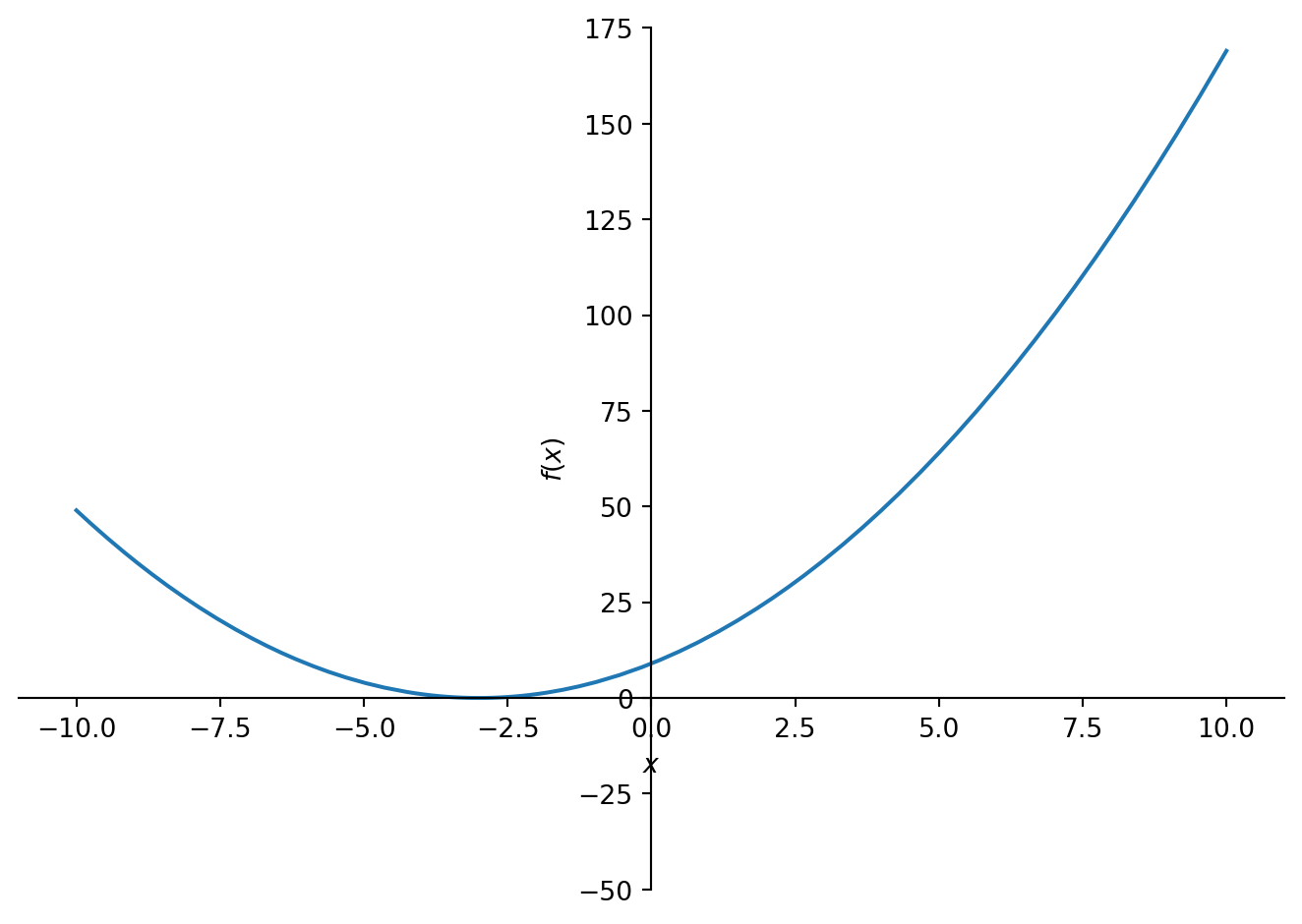
<sympy.plotting.plot.Plot at 0x1051ed6d0>Example 2: Plotting Multiple Mathematical Functions
Example 3: Plotting Multiple Mathematical Functions
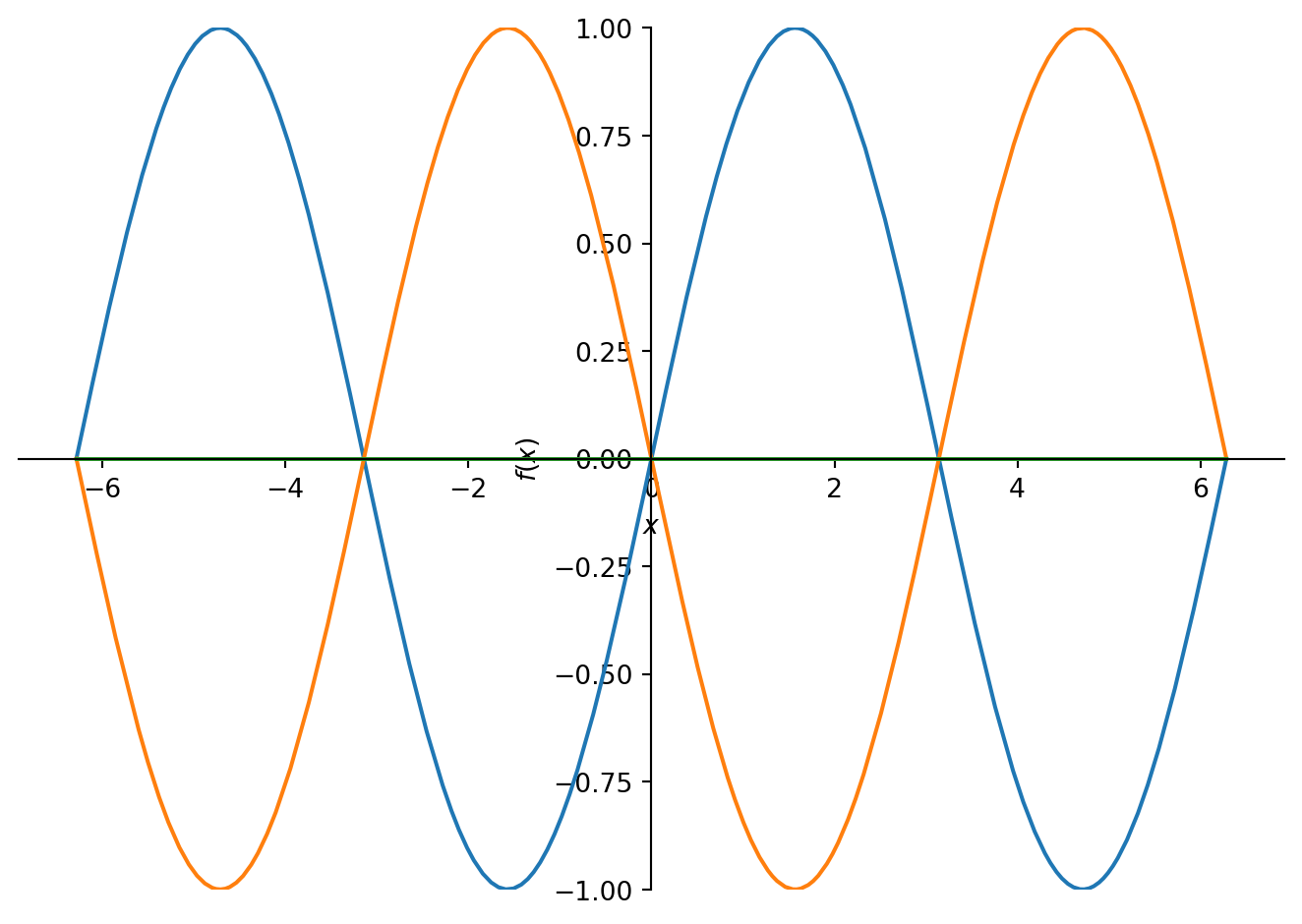
<sympy.plotting.plot.Plot at 0x127467400>Conclusion:
The relationship between mathematical functions and functions in Python revolves around the idea of relating inputs to outputs. Python provides a practical and versatile environment for working with functions, and libraries like SymPy and Matplotlib enhance the capabilities to handle symbolic mathematics and create visual representations of functions. By understanding this relationship, you can leverage Python’s functionality for mathematical computations and visualization, making it a powerful tool for various scientific and engineering tasks.